Pascal's Law
Pascal's Law: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Atmospheric Pressure, Hydraulic Lift,Absolute Pressure and Units Used for Atmospheric Pressure etc.
Important Questions on Pascal's Law
The pressure at the bottom of a tank of water is where is the atmospheric pressure. If the water is drawn out till the level of water is lowered by one-fifth, the pressure at the bottom of the tank will now be
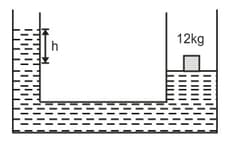
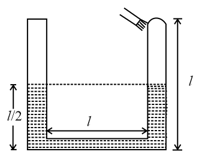
The area of cross-section of the wider tube shown in figure is . If a mass of is placed on the massless piston, the difference in heights h in the level of water in the two tubes is
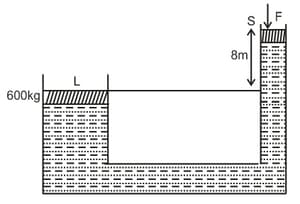
For the system shown in the figure, the cylinder on the left athas a mass of and cross-sectional area of . The piston on the right, at , has cross-sectional area and negligible weight. If the apparatus is filled with oil. Find the force required to hold the system in equilibrium
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A: When you squeeze one end of a tube to get toothpaste out from the other end, Pascal’s principle is observed.
Reason R: A change in the pressure applied to an enclosed incompressible fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and to the walls of its container.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
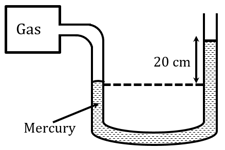
A manometer reads the pressure of a gas in an enclosure as shown in figure. The absolute and gauge pressure of the gas (in of mercury) in the enclosure is
(Take atmospheric pressure = of )
The height of mercury column in a simple barometer is . As the tube is inclined with the vertical at an angle , then length of mercury column along the length of the tube will become
Calculate the barometer reading at a place where atmospheric pressure is . Given that the density of mercury is .
A force of is executed on a hydraulic piston of cross sectional area of . The cross-sectional area of other piston which supports a truck of a tonne weight is [use ]
In a hydraulic lift, compressed air exerts a force on a small piston of radius . Due to this pressure the second piston of radius lifts a load of . The value of is
(Acceleration due to gravity )
The working of hydraulic lift is based on the principle of
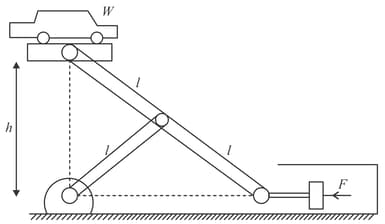
A car hoist is operated by a hydraulic as pictured. Determine compressive force applied by hydraulic to keep the car-weight in equilibrium at given position.
A hydraulic lift is designed to lift heavy objects of maximum mass . The area of cross section of piston carrying the load is What is the maximum pressure the piston would have to bear?
Two vertical conducting cylinders and of different cross sections are connected by a thin tube as shown. An ideal gas is trapped in the cylinders by two airtight pistons of masses and respectively. Initially the pistons are at the same height above the base of the cylinders. If an additional mass of were gently placed on the piston in the cylinder , Which of the following statements correctly describe the new steady state ultimately reached.
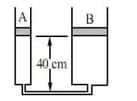
A heavy load is supported on a platform of area by applying a force on a small piston of area The value of for equilibrium is
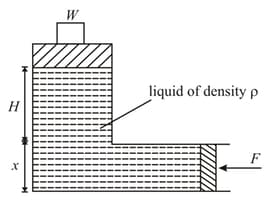
Some amount of water is trapped between two pistons, when can slide without friction in the vertical arms and of an -shape tube. Area of horizontal crosssection of the arm is times of the area of the arm . The piston in the arm is supported on a spring of force constant . In equilibrium, length of tube below the piston in arm is . What maximum additional mass can be gently placed on the piston in the arm so that piston in arm will remain inside the tube ? Density of water is and acceleration due to gravity is .
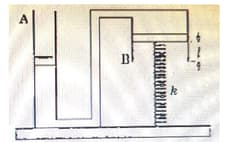
A uniform rectangular narrow -tube has equal arm lengths and base length, each equal to . The vertical arms are filled with mercury up to and then one end is sealed. By heating the enclosed gas all the mercury is expelled and collected at same level as the top most point of the tube. Assume ideal gas and ideal liquid conditions. If atmospheric pressure is , the density of mercury is and cross-sectional area is , then : [Neglect thermal expansion of glass and mercury, surface tension and viscosity effects and assume ]
A dam of the water reservoir is built thinner at the bottom.
Describe the factors determining the pressure exerted by liquids.
Hydraulic press/lift is based on the principle of